Sainik Schools
What is Sainik Schools ?
About Sainik Schools
The scheme to establish Sainik Schools originated in order to serve as an ideal residential educational institution for the deserving intelligent sections of the boys & girls hailing from myriad backgrounds. It enables students to take up an illustrious career as an officer in the Armed Forces of the Nation and other celebrated professions. Moreover, the high levels of physical, mental and intellectual attainments needed for induction into the Officer Cadre of the Defence Services could not be nurtured in the common schools, mainly because of the lack of exposure for defence services. The training imparted in Sainik Schools influences the students in shaping their social attitudes and meaningful approach to life in general in order to emerge as responsible citizens of India and leaders in different walks of life.
Why Sainik Schools
These schools offer a vast array of opportunities to channelize the energies of cadets for constructive purposes. A wide spectrum of co and extracurricular activities ensure complete education and all-round personality development of the cadets. However, if the Cadet is Unable to join the NDA due to any reason, he attains enough proficiency like those who have gone on to become bureaucrats, lawyers, engineers and journalists, holding the Sainik school Flag aloft in all the avenues they endeavoured in.
Who can join Sainik school
Sainik Schools offers admission to Class VI and Class IX for the academic year 2021-22, Admission is based on the performance of candidates in the All India Sainik Schools Entrance Examination (AISSEE). The final selection is based on school-wise, class-wise, category-wise rank in the merit list of the Entrance examination, medical fitness approved by competent Medical authorities and verification of original documents and such other criteria as may be prescribed by the Sainik school society. AISSEE 2021 will be conducted by National Testing Agency (NTA).
Eligibility criteria
For admission to Class VI: A candidate should be between 10 and 12 years as on 31 March 2021 for admission to Class VI, i.e. he/she should have been born between 01 April 2009 and 31 March 2011 (both days inclusive) for admission to the academic year 2021-22.
- Admission for Girls is open for Class VI. Age criteria are the same as boys.
For admission to Class IX:
- A candidate should be between 13 and 15 years as of 31 March 2021, for admission to Class IX, i.e. he/ she should have been born between 01 April 2006 and 31 March 2008 (both days inclusive)
Admission to Class IX is not open for girls:
- He/ she should have passed the Class VIII exam from a recognized school at the time of admission.
Scheme of Examination:
Mode of Examination: Paper pencil on OMR answer sheets for admission to both Class VI and Class IX. Type of Questions: Multiple Choice Questions, Time duration is 150 minutes
Scheme of examination for 6th std:
| Section | Topic | No of questions | Marks for each correct Answer | Total marks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Mathematics | 50 | 3 | 150 |
| B | Intelligence | 25 | 2 | 50 |
| C | Language | 25 | 2 | 50 |
| D | General Knowledge | 25 | 2 | 50 |
| Total | 125 | 300 |
Scheme of examination for 9th std:
| Section | Topic | No of questions | Marks for each correct Answer | Total marks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Mathematics | 50 | 4 | 200 |
| B | Intelligence | 25 | 2 | 50 |
| C | English | 25 | 2 | 50 |
| D | General Science | 25 | 2 | 50 |
| E | Social Science | 25 | 2 | 50 |
| Total | 150 | 400 |
Medium of Examination:
For admission to Class IX:
- English only
- Time duration is -180 minutes
For admission to Class VI:
- English
- Hindi
- Assamese
- Bengali
- Gujarati
- Kannada
- Malayalam
- Marathi
- Odiya
- Punjabi
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Urdu
Exam Syllabus For Class 6:
Mathematics Topics:
- Natural Numbers
- LCM and HCF
- Unitary Method
- Fractions
- Ratio and Proportion
- Profit and Loss
- Simplification
- Average
- Percentage
- Area and Perimeter
- Simple Interest
- Lines and Angles
- Temperature
- Conversion of Units
- Roman Numerals
- Types of Angles
- Circle
- Volume of Cube and Cuboids
- Prime and Composite Numbers
- Plane Figures
- Decimal Numbers
- Speed and Time
- Operation on Numbers
- Complementary and Supplementary Angles
- Arranging of Fractions
Intelligence Topics:
- Questions on Intelligence will be based on analogies (mathematical & verbal), pattern (spatial and mathematical), classification, visual, logical, reasoning etc.
English Topics:
- Comprehension Passage
- Preposition
- Article
- Vocabulary
- Verbs and Type
- Confusing Words
- Question Tags
- Types of sentence
- Tense forms
- Kinds of Nouns
- Kinds of Pronouns
- Correct Spelling
- Ordering of Words in Sentence
- Sentence Formation
- Antonyms
- Synonyms
- Adjectives
- Interjection
- Idiom and Phrases
- Collective Nouns
- Number
- Gender
- Adverbs
- Rhyming Words
- Singular/Plural
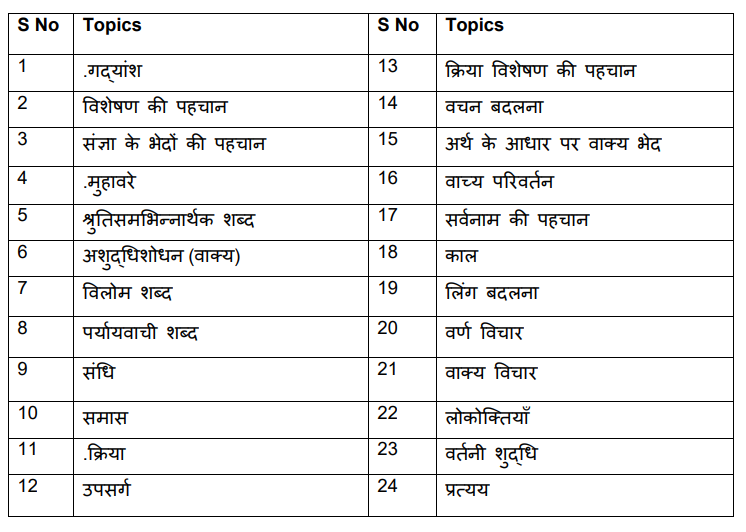
Hindi Topics:
General Knowledge Topics:
- Different Types of Scientific Devices Used in Daily Life.
- Icons and Symbols of India: National Insignia, National Emblem, Sports, Animal etc. (Elementary awareness of such symbols)
- Major Religions of India (Elementary awareness about founder, place of origin, religious books and important ideas)
- Art and Culture (Music, Classical and Folk Dance); Renowned Personalities, Instrumental and Vocal Music, Major Dance Forms
- Defence (Equivalent Ranks in three services, Weapons, Aircraft, Missiles &Warships (Elementary awareness)
- Sports and Games (India & World). Renowned personalities, major competitions and trophies associated with various games
- Super Senses (How do plants and animals sense their surroundings)
- Relationship between Animals and Human Beings
- Taste and Digestion (Basic concepts)
- Cooking and Preserving Techniques
- Germination and Seed Dispersal
- Traditional Water Harvesting Techniques
- Experiment with Water on Everyday Life
- Water Pollution and Microbial Diseases
- Concepts on Mountain Terrain and Lifestyle
- Historical Monuments
- Shape of Earth and Gravitation (Basic concepts)
- Non-Renewable Energy Sources (Fossil Fuels)
- Food, Culture, Habitat, Languages etc of various regions (Basic concepts)
- Names of young ones of different animals
- Functions of Body Parts of Plants and Animals
- International Organizations: Basic knowledge about structure, functioning and objectives of United Nations, World Bank etc.
- Indian Literary and Cultural Personalities: Names and fields of achievements
- Indian Literary and Cultural Awards. (Names of the awards and recent recipients)
- Natural Calamities (Flood and Earthquake)
- Evaporation, Condensation and Water Cycle (Basic concepts)
- Life of Farmers (Farming techniques)
- Tribal Communities and Forest Produce
Exam Syllabus For Class 9th:
Mathematics Topics:
- Rational Numbers
- Linear Equations in One Variable
- Understanding Quadrilaterals
- Data Handling (Bar Graph and Line Graph)
- Squares and Square Roots
- Cubes and Cube Roots
- Comparing Quantities (Percentage, Profit and Loss)
- Algebraic Expressions and Identities
- Area and Perimeters
- Volumes and Surface Areas
- Exponents and Powers
- Playing with Numbers
- Visualizing Solid Shapes
- Triangles ( Pythagoras Theorem)
- Euler’s Formula
- Average, Median, Mode
- Probability
- Pie Chart
- Direct & Inverse Proportions
- Factorizations
- Introduction to Graph
- Unitary Method
- Divisibility Exam
- Triangles (Angle Sum Property)
- Parallel Lines
- Simple Interest and Compound Interest
- Time and Work
- Area and Perimeter of Circles
- Algebraic Expression (Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division)
Intelligence Topics:
- Questions on Intelligence will be based on analogies (mathematical & verbal), pattern (spatial and mathematical), classification, visual, logical, reasoning etc.
English Topics:
- Spotting Errors
- Comprehension Passage
- Antonyms
- Synonyms
- Prepositions
- Articles
- Types of Verbs
- Tense Form
- Narration
- Voices
- Modals
- Confusing Words
- Subject-Verb Agreement
- Correct Spellings
- Order of words in a sentence
- Idioms and Phrases
- Sentence Improvement
- Change of sentence as directed
- Sentence Formation
- Types of Sentences
- Phrase and Clauses
- Kinds of Noun
- Adjectives
- Interjection
- Question Tags
- Adverbs
- Conjunctions
- Conditions
- Comparison of Adjectives
- Personal Pronoun
- Change of Gender
- Change of Number
General Science Topics:
- Fossil Fuel: Coal and Petroleum
- Combustion and Flame
- Cell Structure and Function
- Reproduction in Plants and Animals
- Force, Friction and Pressure
- Sound and its basics
- Reflection and Dispersion of Light
- Metals and Non-Metals
- Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Stars and Solar Systems
- Pollution of Air and Water
- Global Warming
- Micro-Organisms
- Some Natural Phenomenon
- How to find calorific value of fuel?
- Electroplating and Artificial Jewellery
- Relation between types of friction
- Cropping Seasons
- Agricultural Practices
- Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Biosphere Reserves, National Parks and Sanctuaries
- Reaching the age of Adolescence
- Changes during Puberty
- Endocrine Glands and Hormones
Social Science Topics:
- Revolt of 1857 20 Interior of Earth
- Freedom Fighters
- Important Freedom Movements
- Social and Caste Reforms
- Resources and sustainable development
- Rock cycle of water cycle
- Pressure and Wind System
- Land Soil and Water Resources
- Minerals and Power Resources
- Indian Constitution and Secularism
- Importance of Parliament
- Types of Agriculture
- Types of Government and different tiers of Government
- Understanding Markets
- Elections
- Role of Government in Health
- Delhi Sultanate
- Mughals
- Bhakti and Sufi Movement
- Climate Change
- Earthquakes and Major Land Forms
- Types of Rainfall
- Major Grasslands
- Types of Forests
- Means of Transport
- Communication
- Life in deserts
- Panchayat System
- Local Self Government
- Law and Social Justice
- Judiciary and Criminal Justice System
- Marginalisation
- Public Facilities
- Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
- Industries
- Human Resources
- Changes in the Arts